View by Category
Published
, Published online: 09 February 2026
, doi: 10.37188/lam.2026.018
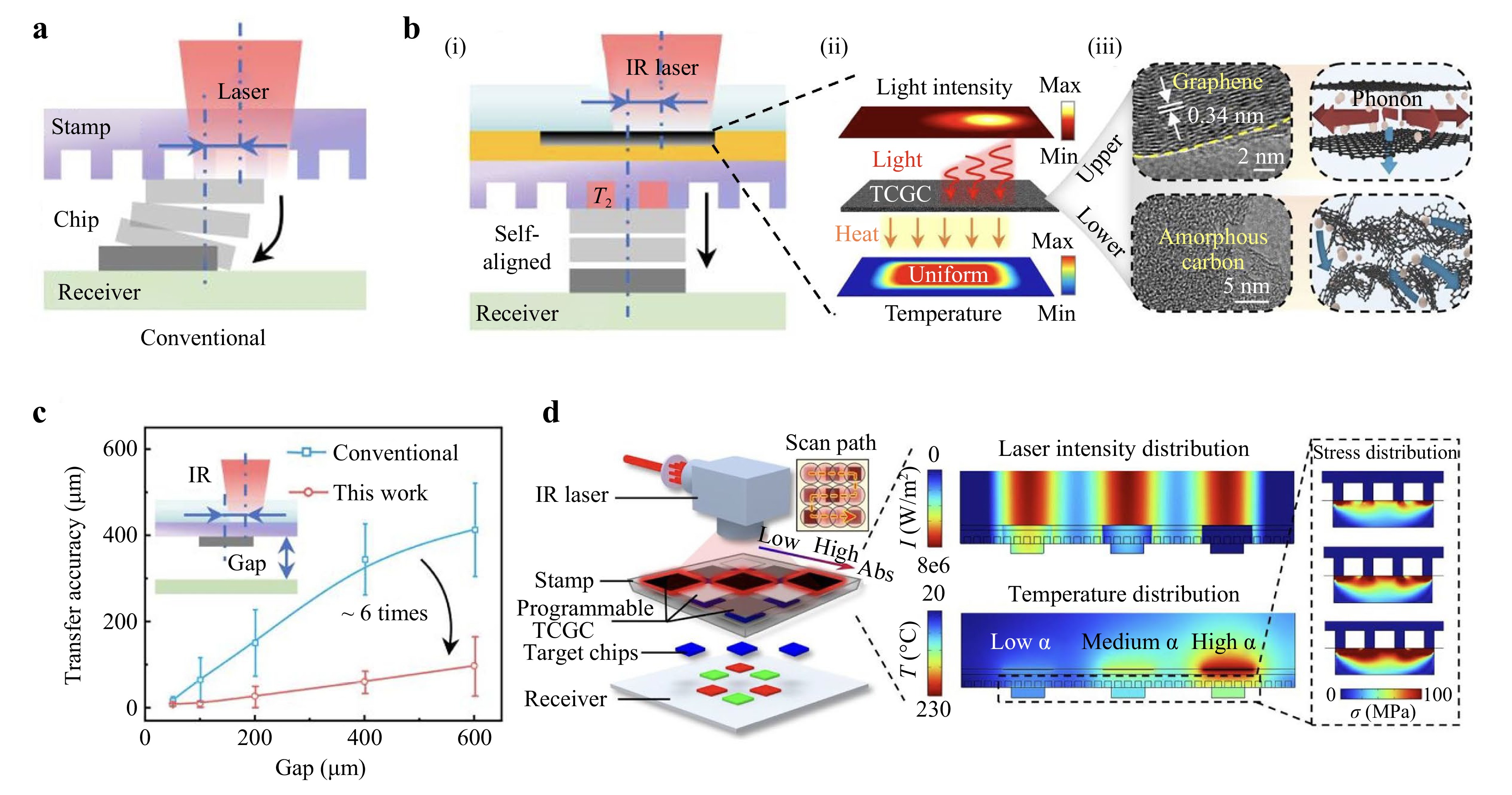
Gradient-graphene-enabled directional photothermal regulation is proposed and demonstrated to achieve uniform heat distribution in the laser-sensitive layer, thereby enhancing the accuracy of self-aligned laser transfer printing.
Published
, Published online: 30 January 2026
, doi: 10.37188/lam.2026.012
Patterned photonic crystals that exhibit structural colours attract considerable attention owing to their exceptional color saturation and variability. A unique paintable helical photonic architecture featuring both multi-stability and dynamic light-actuation is proposed. The method shows great potential for applications in anti-counterfeiting, information encryption, and smart windows.
Published
, Published online: 09 October 2025
, doi: 10.37188/lam.2025.066
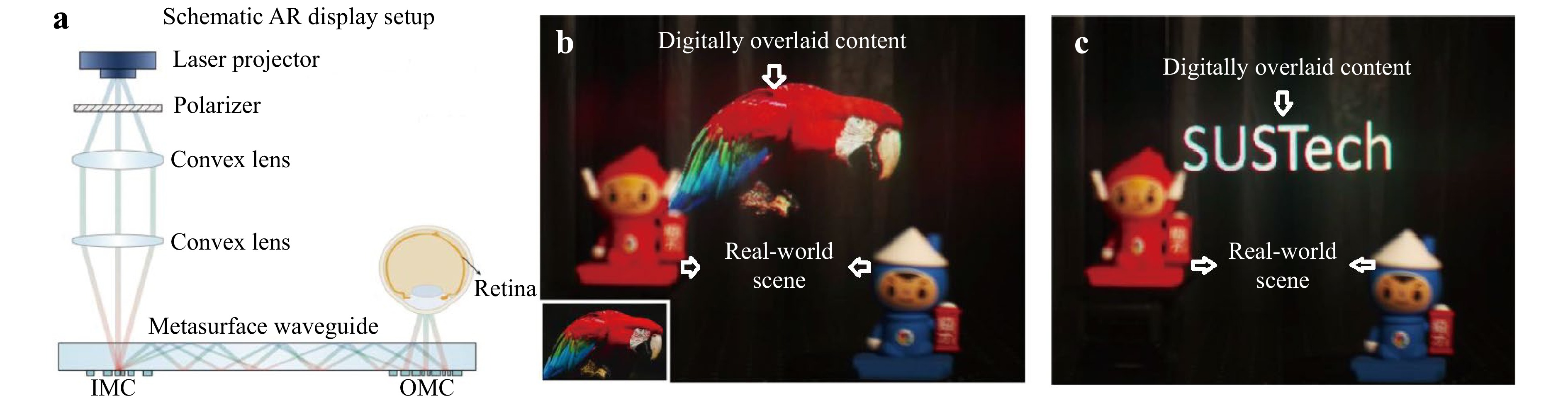
A novel approach is presented for correcting chromatic aberration in full-color AR using an inverse-designed metasurface, enabling improved color accuracy and uniformity in diffractive waveguide combiners, with potential for more compact and efficient AR glasses.
Published
, Published online: 20 January 2026
, doi: 10.37188/lam.2026.010
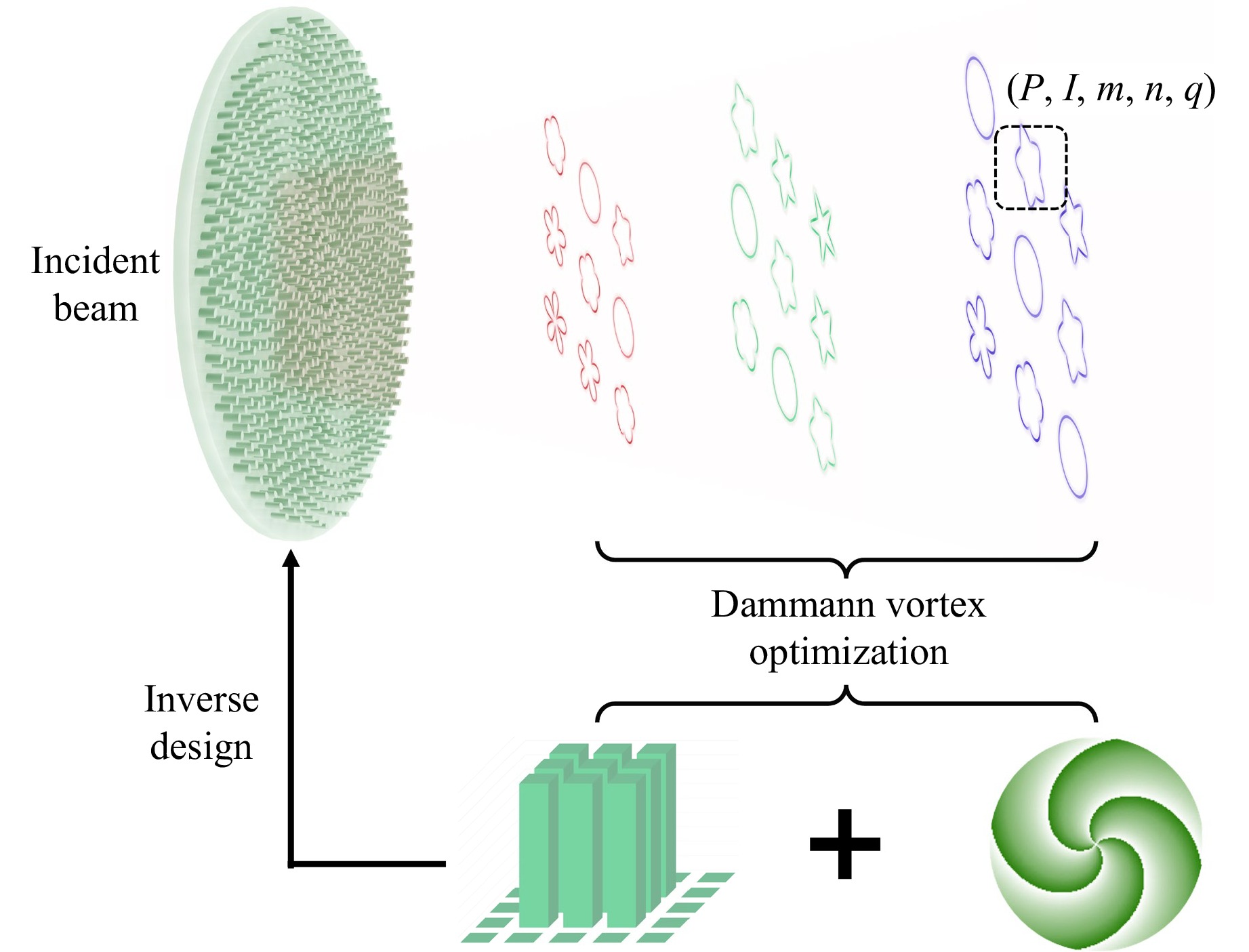
Multidimensional light-field control is opening new frontiers in photonics. Recent breakthroughs in metasurface design and the integration of Dammann optimisation with spin-decoupled phase modulation enable the simultaneous manipulation of phase, amplitude, polarisation, and orbital angular momentum to project information into three-dimensional space. This paradigm shift towards full-parameter control in stereoscopic volumes is promising for revolutionising applications from high-capacity optical communications to secure encryption and parallel computing, marking a significant advancement in integrated photonic systems.
Published
, Published online: 10 December 2025
, doi: 10.37188/lam.2025.083
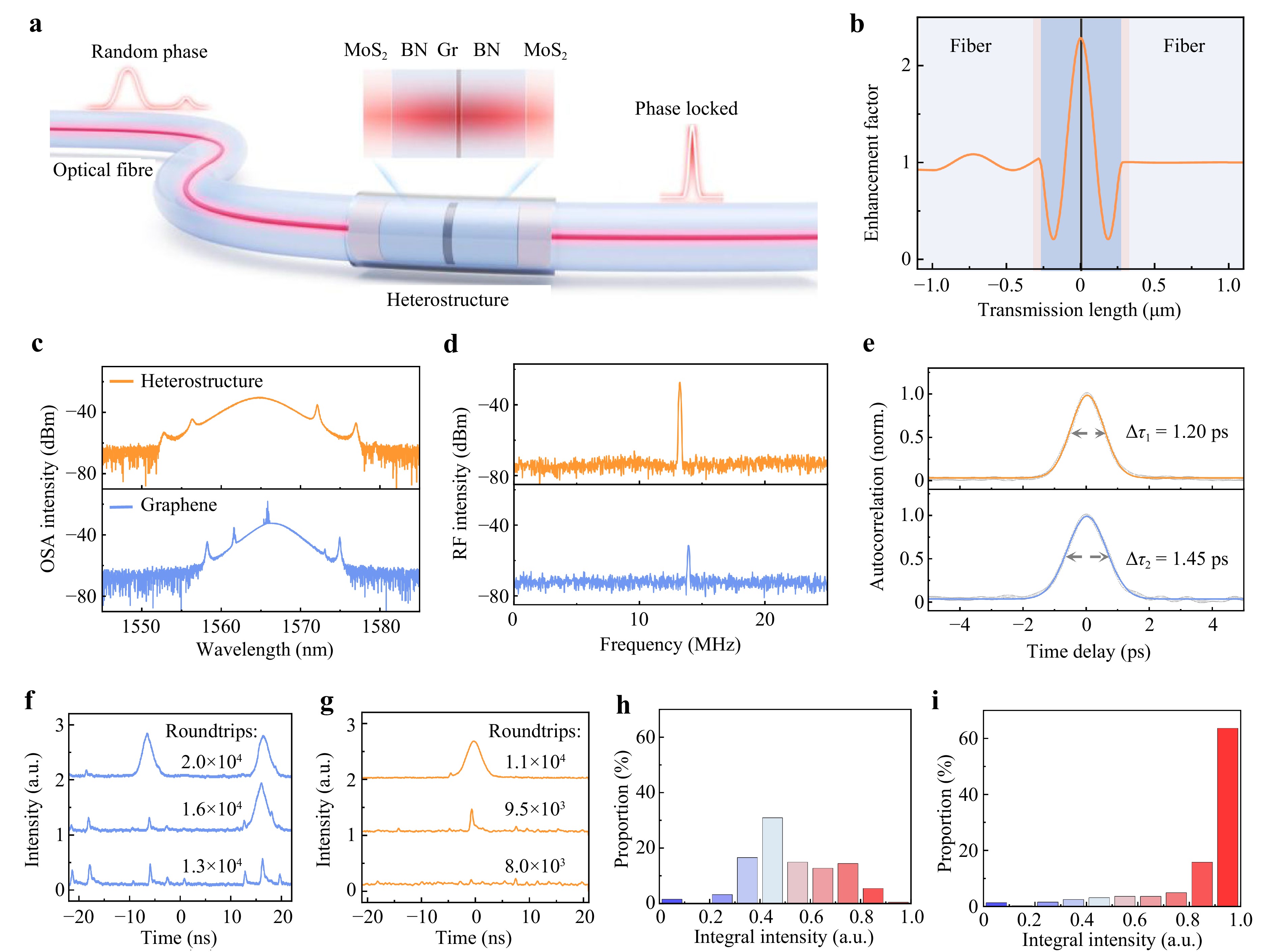
A robust saturable absorber that integrates MoS2-BN-graphene-BN-MoS2 nanocavity on fibre is proposed and demonstrated. The proposed absorber lowers saturation intensity to 22 MW cm−2, raises polarisation tolerance to 85%, and stabilises single-soliton mode-locking in all-fibre lasers. This work provides a practical and high-performance solution for achieving stable mode-locking in all-fibre lasers, effectively overcoming the inherent limitations of conventional 2D saturable absorbers.
Published
, Published online: 04 December 2025
, doi: 10.37188/lam.2025.085
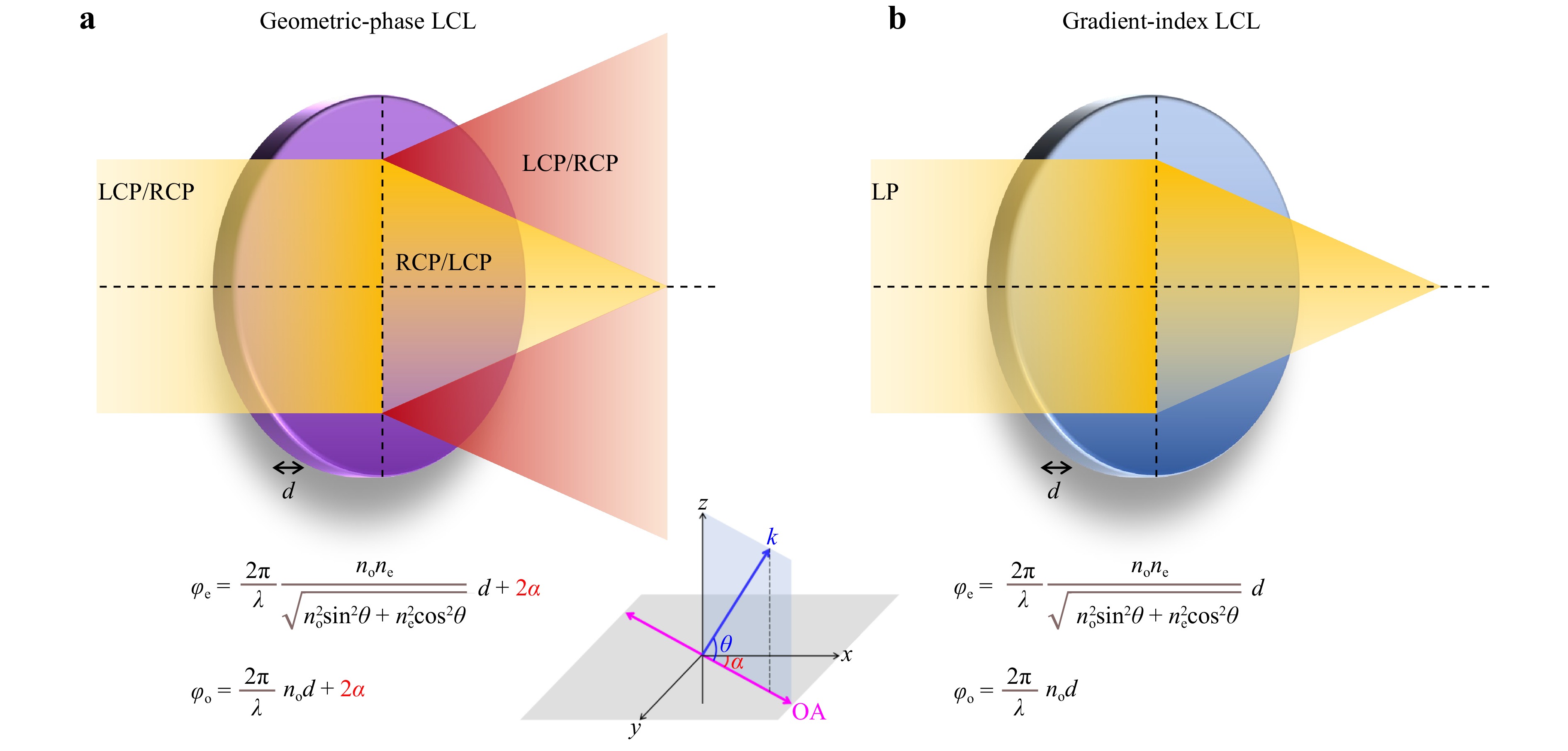
Liquid crystal lenses can be achieved with either geometric phase or gradient refractive index. Which solution will ultimately prevail is open to debate. This article aims to provide a theoretical background, review the latest seminal research findings, and shed light on their pros and cons from multiple perspectives.
Beyond conventional VCSELs: Emerging directions with colloidal quantum dots and geometry engineering
Published
, Published online: 03 December 2025
, doi: 10.37188/lam.2025.084
Recent advances have highlighted new directions for vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs). Engineering the device architecture enabled electrically pumped surface-emitting amplified spontaneous emission from colloidal quantum dots, while non-circular cavity geometries enhanced power scaling, coherence control, and polarization stability. These breakthroughs broaden VCSEL research, pointing to customizable, application-specific devices.
Published
, Published online: 25 November 2025
, doi: 10.37188/lam.2025.082
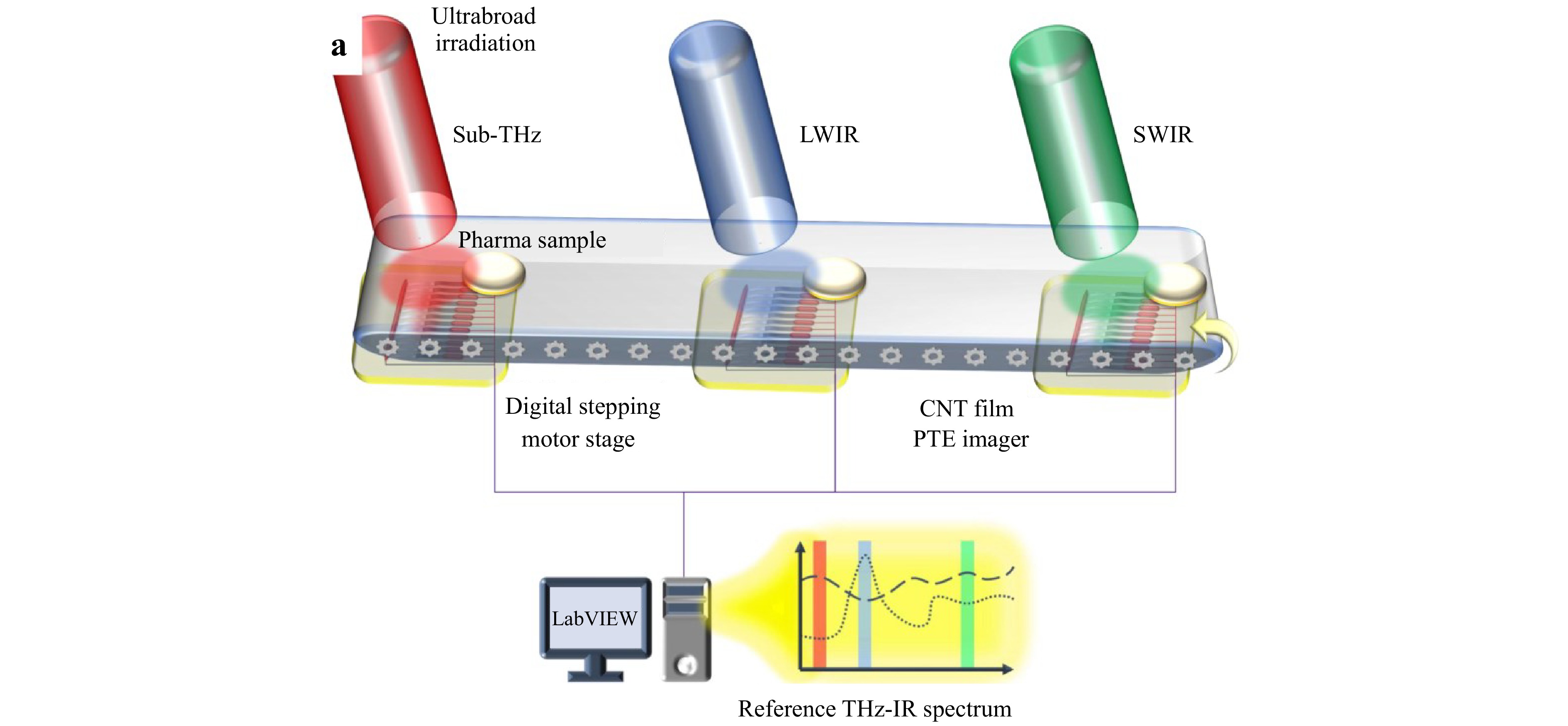
A non-destructive in-line dynamic detection system based on carbon nanotube thin film photo-thermoelectric imager has been developed. Utilizing ultra-broadband sub-terahertz-infrared multi-band light monitoring, it achieves efficient, contactless dynamic visual detection of ingredients and foreign matter in tablets.
Published
, Published online: 12 November 2025
, doi: 10.37188/lam.2025.081
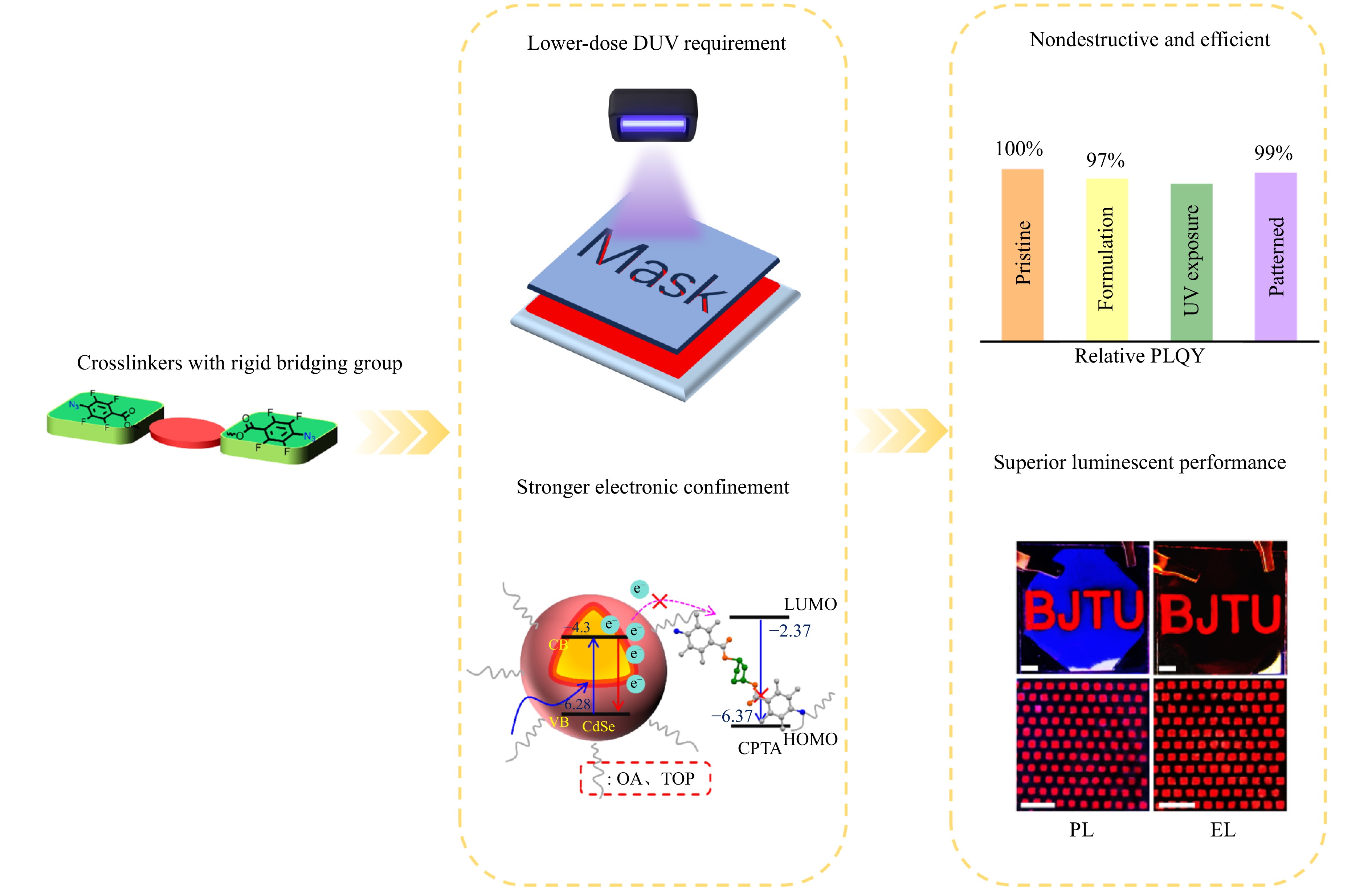
A direct photolithography approach using rigid crosslinkers was developed for the precise patterning of quantum dot (QD) layers, producing high-resolution RGB arrays with pixel sizes down to 1 μm. This strategy suppresses QD degradation typically associated with conventional high-UV photolithography while enhancing electron confinement within the QDs, thereby preserving their luminescent properties. As a result, high-performance patterned red QLEDs were successfully fabricated.
Published
, Published online: 06 November 2025
, doi: 10.37188/lam.2025.070
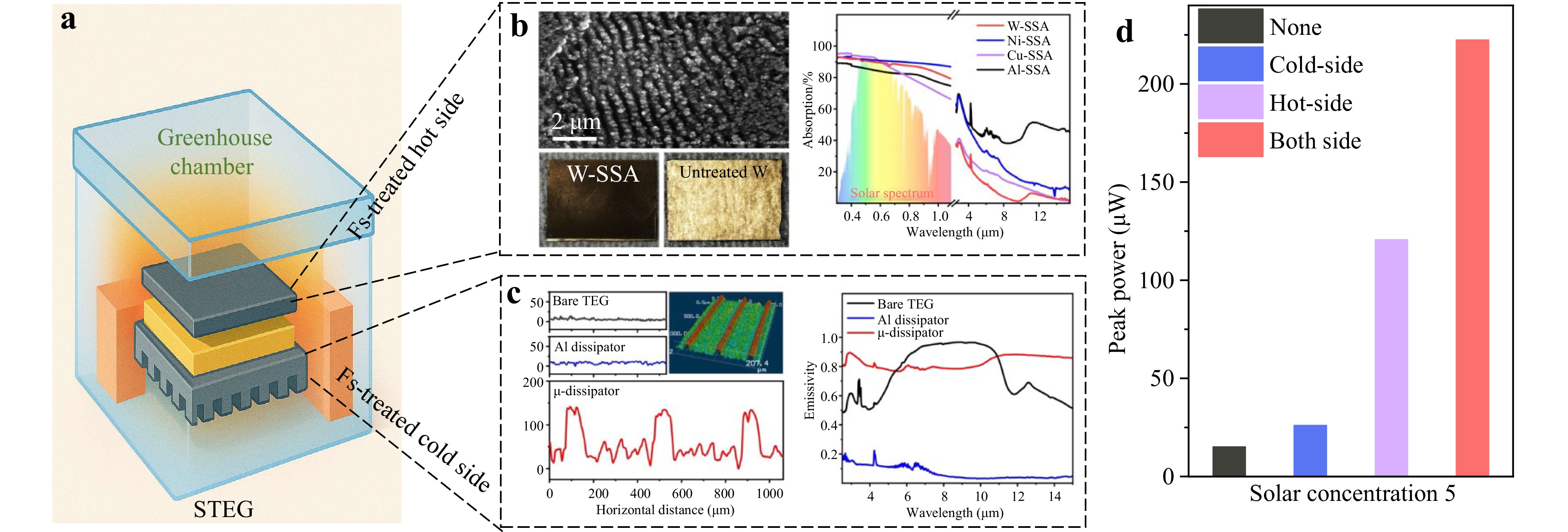
Femtosecond laser processing enables the fabrication of high-absorption, low-emissivity solar absorbers and highly efficient microstructured heat sinks for heat dissipation in solar thermoelectric generators (STEGs), leading to a 15-fold increase in output power.
- First
- Prev
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Next
- Last
- Total:3
- To
- Go





 Email
Email RSS
RSS